2.1.THE AVERAGE ( Arithmetic mean)
Dear students, the topic of measures of central tendency will help you understand the basic concept of average as mentioned below in the following headlines :
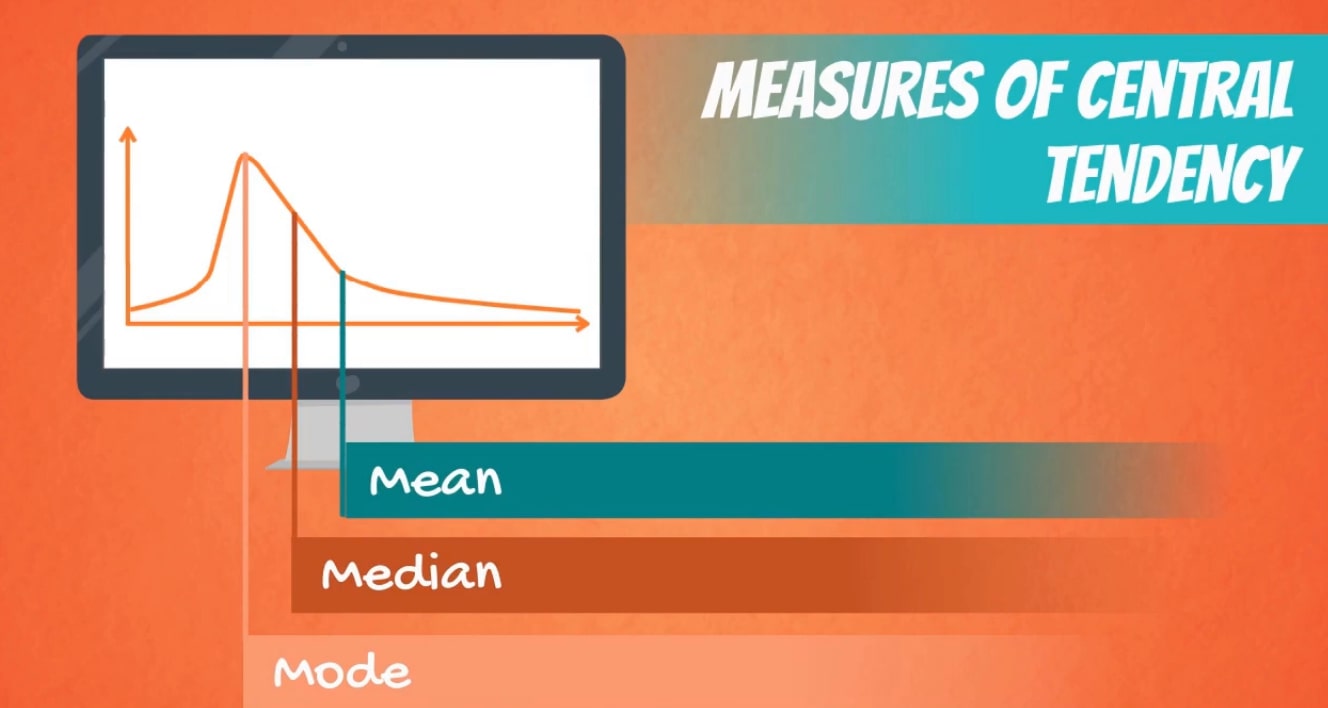
. MEASURE OF CENTRAL TENDENCY
2.1 The Basic Concept of an Average
2.2 Arithmetic Mean
2.3 Median
2.4 Mode
MEASURES OF CENTRAL TENDENCY (AVERAGE)
The Average:
Average is the single value which represents the characteristics of whole data set.
According to statistical.com
An average is the representative value of whole set of data.
The criteria of satisfactory average/good qualities of average
⇨ Simple to understand
⇨ Easy to interpret
⇨ Easily and quickly calculated
⇨ Based on all observation
⇨ It explains the masses of all observation
Kinds of average
1 The Arithmetic mean/mathematical mean (ideal average)
2 The median => the average of location or position Median means exact two parts of data
3. The Mode
Arithmetic means:
It is the sum of all observation divided by total numbers of its units is called Arithmetic Mean.
Formulas:
= Single series
x = ∑Χ / n
= Discrete series
x = ∑ƒx / ∑ƒ
Find out the value of AM from the given data (ungroup)
|
X: |
12 |
10 |
9 |
16 |
20 |
08 |
10 |
13 |
16 |
Solution:
x : 12 10 9 16 20 08 10 13 16 = 144
∑Χ = 114
n = 9
Formula of mean: =
x = ∑Χ / n
114/9
= = 12.6 answer.
Find out the AM from the given data(group)
|
Classes:x |
1 – 5 |
6 - 10 |
11 - 15 |
16 – 20 |
21 – 25 |
|
ƒ |
6 |
2 |
4 |
10 |
3 |
solution
|
age of students |
ƒ |
MP(x) |
ƒΧ |
|
1 – 5 |
6 |
1+5=6/2=3 |
18 |
|
6 – 10 |
2 |
8 |
16 |
|
11 – 15 |
4 |
13 |
52 |
|
16 – 20 |
10 |
18 |
180 |
|
21 - 25 |
3 |
23 |
69 |
|
|
ķ 25 |
|
∑ƒ 335 |
By applying the formula: ∑ƒx / ∑ƒ
∑ƒx = 335
ķ= 25
x= 335/25
ans=13.4
x= the average students age is approximately 14